World’s Largest Water Pumps: Mega-Pumps Protecting Cities and Infrastructure

When it comes to moving water on a massive scale, ordinary pumps won’t cut it. Around the world, engineers have built mega-pumps – giant pumping stations capable of moving rivers of water in seconds – to protect low-lying cities from floods, support huge hydro projects, and manage water for millions of people.
In this article, we’ll dive into some of the world’s largest water pumps, explore why they’re needed, and see how their mind-boggling capacity compares to the pumps we use in everyday life.
Pumping Titans: The Largest Water Pumps in the World
When we talk about “big pumps,” we’re not just talking about something you'd install in a commercial boiler room—we’re talking engineering giants that shift rivers, protect entire cities, and keep millions of people safe from flooding. These are the titans of water movement: pumps that can drain Olympic-sized swimming pools in seconds and hold back the sea during storms. From flood control in the Netherlands to storm protection in New Orleans and tidal defence in Venice, these mega-pumps are essential to the survival of some of the world’s most vulnerable regions. Let’s take a look at where they are, what makes them so powerful, and why they matter more than ever in a changing climate.
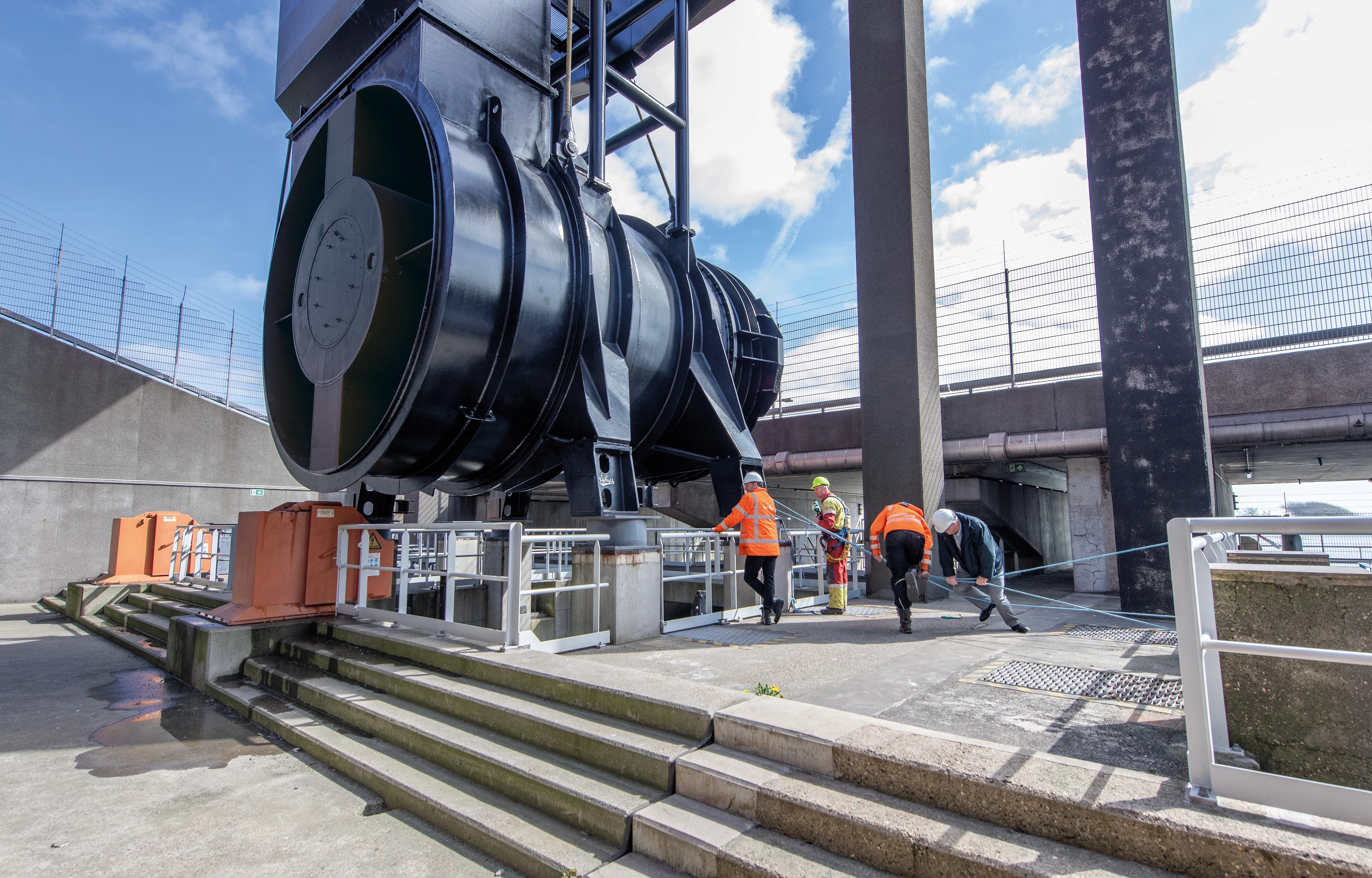


Ijmuiden Pumping Station produced by Pentair
1. IJmuiden Pumping Station (Netherlands) – Europe’s Giant Flood Control Pump
The largest capacity pumps in the world by volume.
Gemaal IJmuiden, Netherlands: The IJmuiden pumping station, near Amsterdam, is one of the world’s most powerful flood control facilities. Its six huge pumps defend the low-lying western Netherlands by pumping excess water from canals into the North Sea. Two “super pumps” were added in 2004, each handling 50 cubic meters of water per second (that’s 50,000 litres every second!) . Manufactured by Pentair Fairbanks Nijhuis, these pumps are so large that each has a 4-meter diameter impeller and weighs about 120 tons – roughly the height of a three-story building. In fact, they earned a Guinness World Record for the largest capacity pumps on the planet.
Why such a huge pump system is needed:
Much of the Netherlands is below sea level, so controlling water is a matter of national survival. IJmuiden pumps around 1 billion cubic meters of water out to sea annually, keeping Amsterdam’s waterways and surrounding polders from overflowing. Without it, heavy rains and river flows would raise water levels in the canals, threatening floods across cities and farmland. The station’s innovative pumps use efficient permanent-magnet motors and variable-speed drives, meaning they can quietly speed up or slow down to match the water flow. This ensures Western Netherlands stays dry – if those pumps were switched off, large areas could gradually end up underwater.
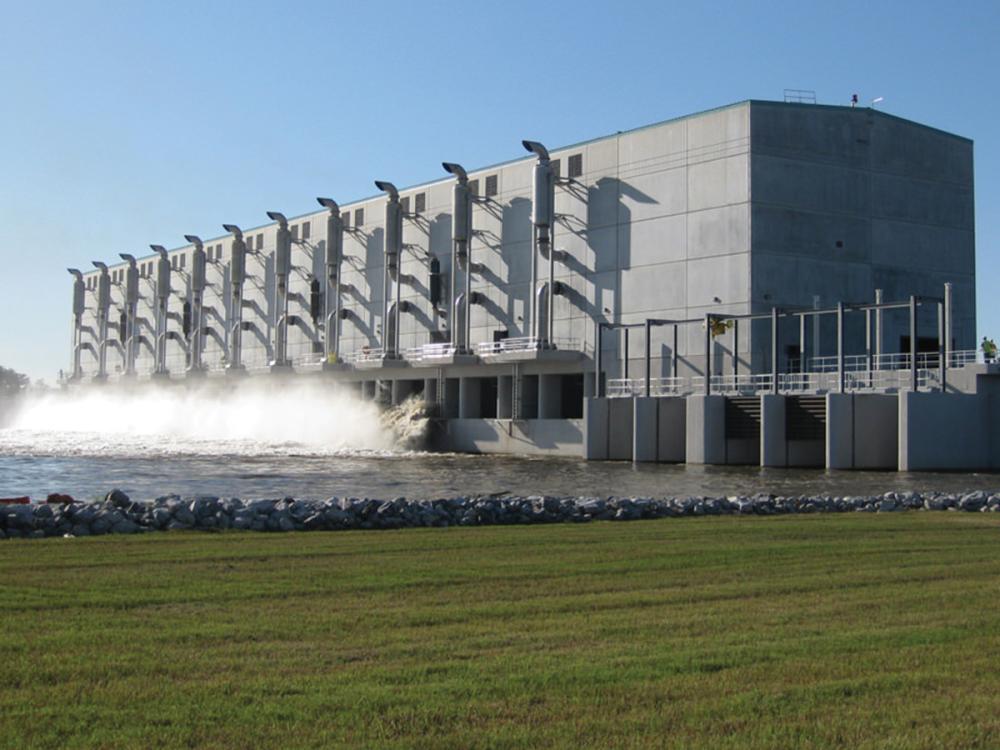


New Orleans Flood Defence - The WCC
2. West Closure Complex (New Orleans, USA) – World’s Largest Drainage Pump Station
World’s Largest Drainage Pump Station
New Orleans Flood Defense: After Hurricane Katrina, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers built the West Closure Complex (WCC) near New Orleans – the largest drainage pumping station in the world. This massive pump station protects the city’s West Bank from storm surge flooding. It features 11 enormous vertical pumps driven by 5,400 horsepower Caterpillar diesel engines, capable of ejecting about 20,000 cubic feet of water per second (around 566 m³/s) when all pumps are running. That’s on the order of 150,000 gallons every second being pushed out to sea.
To picture it, imagine emptying two Olympic swimming pools in a single minute – that’s how much water these pumps can move.
How it works and why it matters:
The WCC includes a huge sector gate across the canal – during a hurricane, the gate closes to block storm surge from Lake Borgne. Once closed, however, any rainwater falling inside the city must be pumped out over the gate. That’s where the 11 mega-pumps come in: they literally lift the city’s stormwater over the flood barrier, dumping it into surrounding wetlands. Without these pumps, neighbourhoods on the West Bank of New Orleans would have no way to drain during big storms, causing catastrophic flooding even with the levees intact. The pumping station, a $1 billion (or ~£773 million at the time of writing, but that doesn’t have the same ring) engineering marvel, is built to withstand 100-year storms, high winds, and even stray barges colliding with it. It’s a vital safety net that proved its worth during hurricanes, keeping low-lying communities dry when nature throws its worst at them.


New Orleans Flood Defence - The WCC
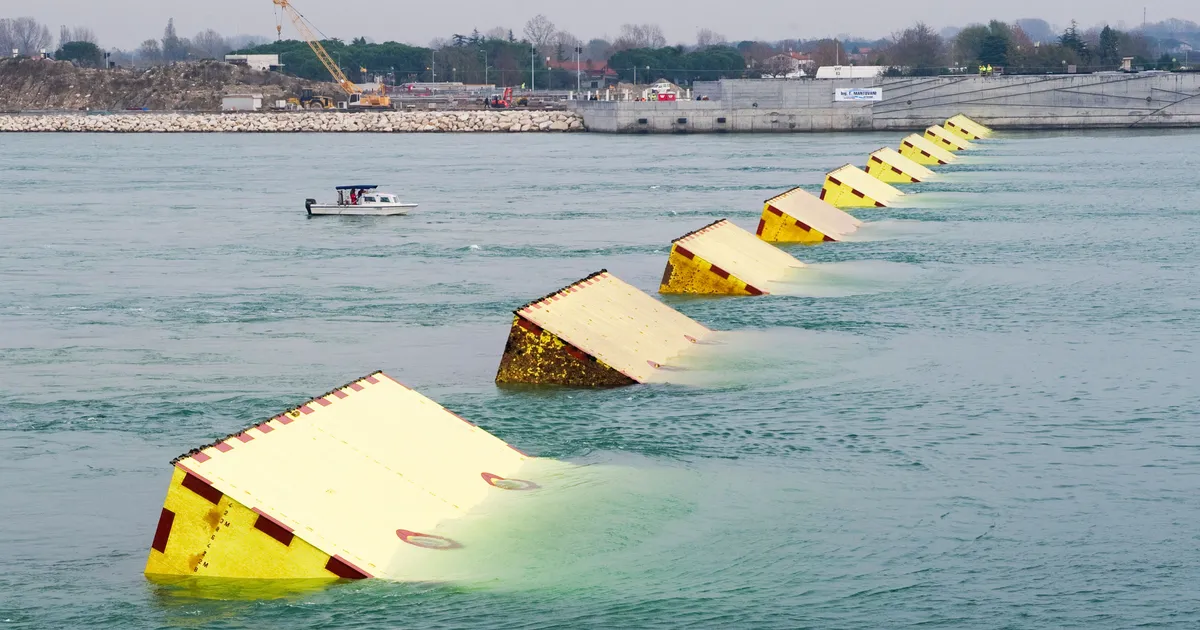
3. MOSE Project (Venice, Italy) – Giant Gates that “Pump Out” the Sea
Venice faces a very different flooding challenge –
The acqua alta, or high tides, periodically inundate the historic city. The MOSE Project is an ingenious system of 78 large floodgates at the inlets of the Venetian Lagoon. While not pumps in the traditional sense (they’re more like hinged barriers), pumps and compressed air are central to how MOSE works. Before a predicted high tide, huge compressors pump air into the hollow steel gates to force out the water and make them buoyant, causing the gates to rise up out of the seabed. Once raised, these metal barriers seal off the lagoon from the Adriatic Sea, keeping Venice dry even when tides reach well over a meter above normal. After the tide passes, the air is released, and the gates fill with water again, lowering back into their underwater housings.
Protecting a city of canals: MOSE is designed to protect Venice from tides as high as 3 meters (nearly 10 feet), higher than the devastating 1966 flood. Without it, Venice would increasingly suffer damaging floods – in 2019, an extreme tide swamped 85% of the city. When waters rise to ~1.3 m or more, authorities activate MOSE to hold the sea back.
Think of the system as a giant pumping mechanism in reverse:
Instead of pumping water away, it pumps air to push a barrier up. It’s a remarkable innovation and one of the largest flood defence projects ever built. Thanks to MOSE, St. Mark’s Square can stay dry during storms that used to send tourists wading through knee-deep water. In the long term, this project is crucial – without it, rising sea levels and storm surges could render parts of Venice uninhabitable.
Although, in recent years, it has garnered criticism on its efficacy, so they're not quite out of deep water just yet.
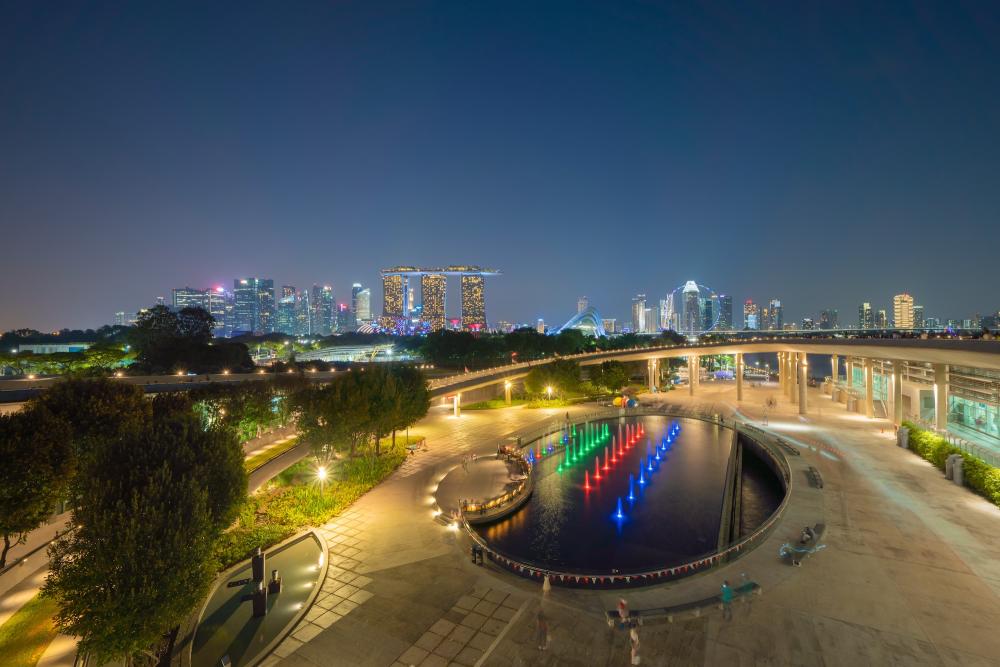


Beautifully lit Marina Barrage at night.
4. Marina Barrage (Singapore) – Urban Flood Control and Water Supply Dam
Marina Barrage, Singapore:
In the heart of Singapore, Marina Barrage serves a dual purpose as a tidal dam and recreation spot – but beneath its park-like surface lies a set of seven powerful pumps that can each move 40 m³/s of water. Together, the pumps can discharge up to 280 m³ per second (that’s 280,000 liters every second) from the freshwater Marina Reservoir to the sea. The barrage has nine crest gates that open during low tide to let excess rainwater flow out by gravity. If a heavy rainstorm coincides with high tide (when the gates can’t be opened without sea water coming in), the giant pumps kick on to flush excess water from the reservoir into the ocean. Each pump is driven by a 1.6 MW electric motor – about the power of 2,000 horsepower – more than enough to keep downtown Singapore from flooding.
A 3-in-1 project:
Marina Barrage was built in 2008 as Singapore’s first urban reservoir dam, turning Marina Bay into a freshwater lake for drinking water supply while also doubling as flood control . On sunny days it’s a popular picnic spot with a scenic rooftop park, but its true value shows during monsoon rains. Why it’s needed: Singapore’s city centre used to suffer flash floods in low-lying areas like Chinatown and Little India.
Now, if torrential rain threatens to overwhelm the drainage system, Marina Barrage’s pumps can drain the stormwater out to sea even when natural tidal flow can’t. This prevents flooding of the city’s financial district and residential neighbourhoods. Essentially, the barrage is a safety valve for the island’s drainage – without it, heavy downpours at high tide could overflow Singapore’s rivers and canals, causing costly flood damage.
(Fun fact: The “Pump House” building at Marina Barrage – marked clearly by its signage – houses all seven massive pumps used during storms.)
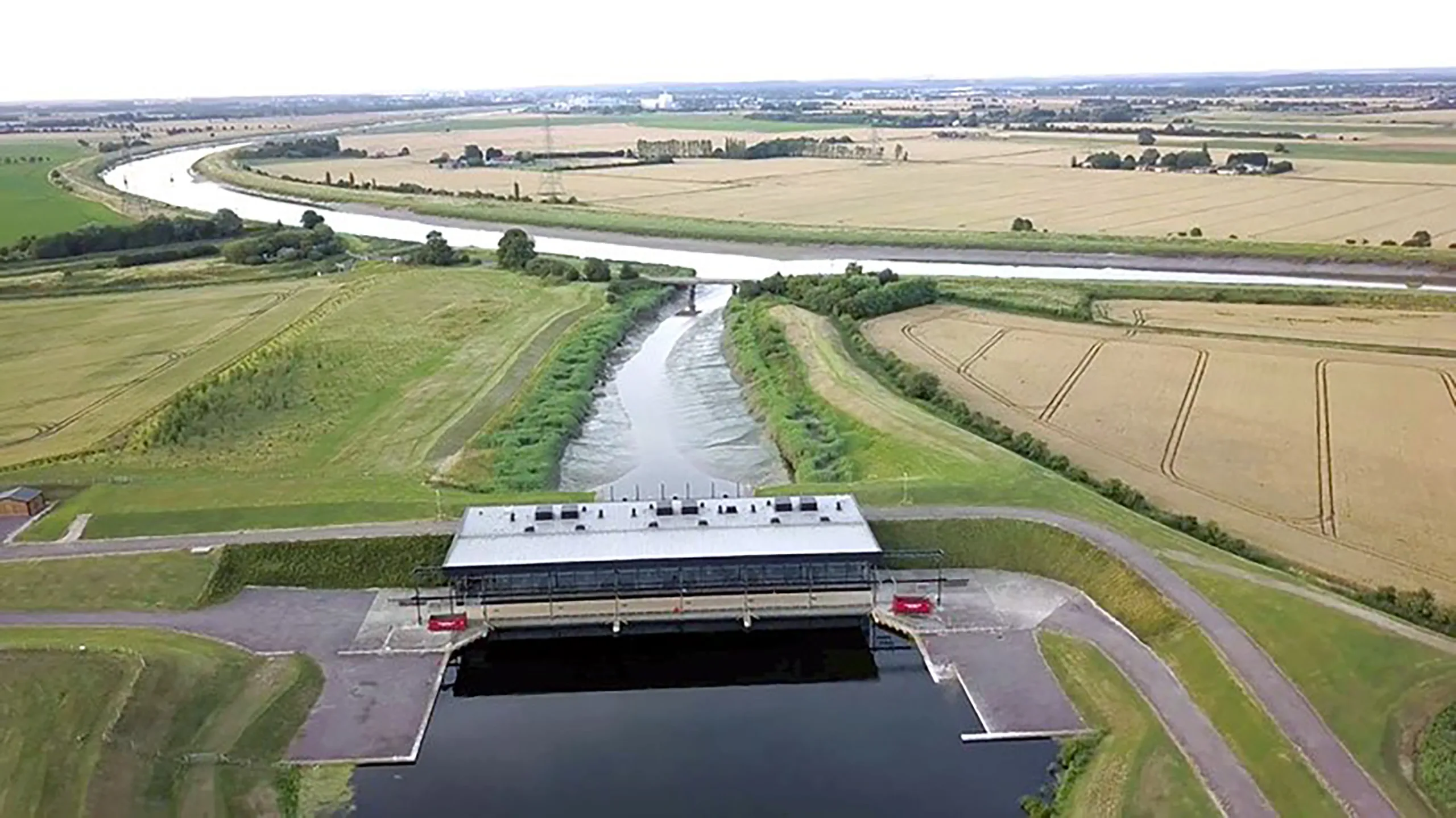


St Germans Pumping Station in Norfolk
Honourable Mention - St Germans Pumping Station, Britain's Biggest Pump
Okay, it's not REALLY an honourable mention in the grand scheme of pumps, but we felt like it's all good talking about these mammoth pumps elsewhere in the world but what about something a bit closer to home for us as a UK-based company?
The Largest Water Pump in the UK
The UK’s largest water pumping station is found in the Cambridgeshire Fens – an area of low, flat land that, like the Netherlands, relies on pumps to stay dry. The St Germans Pumping Station opened in 2010 near King’s Lynn and is the biggest in England. It contains six huge submersible pumps that can shift up to 100 cubic meters of water per second (100,000 litres each second at full throttle).
In real terms, running all six could empty an Olympic-sized swimming pool in just 25 seconds! The station lifts water from the Middle-Level Drain (the main drainage channel for the Fens) up into the tidal River Great Ouse, from where it flows out to the North Sea. Each pump is a giant volute pump built by KSB, powered by an ABB 1.25 MW drive, capable of moving about 16.7 m³/s independently.
Why the Fens need it:
They are reclaimed marshes turned into fertile farmland. They sit at or below sea level, and rainfall or river water doesn’t drain naturally. Without pumping, the Fens would revert to wetlands, putting homes, farms, and roads under water. The St Germans station keeps 700 square kilometres of land (including 25,000 properties and vast farms) safe from flooding. In early 2024, after heavy winter storms, the station was running harder than ever – at one point discharging 77 m³/s continuously, the most in its history. Even at that rate (three-quarters of its capacity), it was enough to fill an Olympic pool every 30 seconds, showing how extreme the weather had been.
Thanks to this pumping station, towns in the Fens remained dry while nature threw a downpour at them. If it hadn’t been for that storm, large parts of Cambridgeshire and Norfolk would have been underwater, reminding us how vital these engineering marvels are for everyday life in low-lying Britain.
From Mega-Pumps to Everyday Solutions: How Do They Compare?
The scale of these mega-pumps is astonishing – moving millions of litres in a blink. But most of us will (thankfully) never need a pump that can drain a city or hold back the ocean. Still, the same principles of moving water apply on a smaller scale, whether it’s keeping a basement dry or supplying water to a building.
At Complete Pump Supplies, we offer a full range of pumps for domestic, commercial, and industrial needs. While they’re much smaller than the giants above, they are designed to keep your home or business safe and dry using similar technology.
Calpeda NMS4 Series (End-Suction Centrifugal Pumps):
If the IJmuiden pump is a giant version of a centrifugal pump, the Calpeda NMS4 is its everyday cousin. These robust pumps are used for clean water supply, heating & cooling systems, and irrigation. For example, a model like the Calpeda NMS4-80/400 can deliver high flow rates (on the order of a few hundred litres per minute) and handle significant pressure for moving water around buildings or farms.
In plain terms, that’s perfect for boosting water pressure in a tall office block or circulating water in an industrial building. It’s a far cry from 50,000 L/s, but when you need reliable flow for your facilities, a Calpeda pump is a workhorse that gets the job done.
(For context: 1000 litres per second would be overkill for a building – a Calpeda NMS4 might pump around 100 litres per second at most, which is plenty to supply a network of taps, showers, or sprinklers.)
This series is known for quiet operation and efficiency – echoing the design priorities of the big pumps, just on a human scale.
Lowara Minibox (Compact Lifting Station):
On the smaller end, consider a scenario many homeowners face – a basement bathroom or rainwater sump that sits below the main sewer line. Gravity alone can’t move that wastewater uphill, so you’d use a packaged pump station like the Lowara Minibox.
This compact unit includes a submersible pump (Lowara’s DOC 3 series) capable of handling around 135 litres per minute (or a mighty ~2.25 litres a second) with a max head up to 6.6 meters.
The Minibox might not save a city, but it can save your basement from flooding by automatically pumping out water when it collects (for instance, during heavy rain or when a washing machine drains in a cellar). It’s a mini version of those grand pumping stations – instead of six monster pumps, it might have one little pump, and instead of a river, it handles your household’s excess water.
But the peace of mind it provides is similar: you know that even if water wants to accumulate where it shouldn’t, the pump will kick in to move it out to where it’s safe.
We offer the Lowara Minibox, similar sump pumps, and sewage lifting stations ideal for homes and small businesses.
They’re easy to install and work automatically, so you can forget they’re there – until they quietly prevent a flood in your utility room!
Linking the scales
It’s fascinating to think that the same basic pump types – centrifugal pumps, axial flow pumps, submersible pumps – are used in mega-projects and the pumps we sell for everyday use. The difference is mostly scale and engineering detail. The pumps at Marina Barrage, for example, are essentially very large axial flow pumps (great for high flow and low pressure), not unlike the smaller submersible flood pumps we stock for drainage, which just scaled up tremendously.
The powerful centrifugal pumps at St Germans are similar in concept to a Calpeda NMS4 or any standard water pump but enlarged and engineered to handle fish, weeds, and huge volumes without clogging.
Finding the Right Pump for You
While you (hopefully) never need to move water by the Olympic pool, it’s good to know there are pumps designed for every purpose. Complete Pump Supplies can help you choose the right pump for your needs – whether it’s a sump pump to keep your home dry, a booster pump to improve your shower pressure or an industrial pump for a factory process. The mega-pumps we’ve discussed are extreme examples of what pumps can do. But they remind us that, big or small, pumps are unsung heroes of modern life: protecting us from floods, delivering us clean water, and quietly doing the heavy lifting so that we can go about our lives rain or shine.
Interested in seeing what’s available?
Feel free to browse our range – from the mighty Calpeda NMS4 series for commercial applications to handy Lowara Minibox units for domestic setups – and get in touch with our team for any advice.
We’re here to help, whether you’re managing critical infrastructure or just your own backyard!